When executed, the SWMM Actions dialog
appears. The General tab is presented first. Two
Carlson files are required for the interface, a surface (.tin) file
and a network (.sew) file. To create a .sew file, input the storm
water management system using the Create Sewer Structure
command found in the Network dropdown of the Hydrology
module. It's important to note that Carlson only transfers
rain event data generated by the SCS Method. If the SCS
Method is inappropriate for the system, the user may input other
types of rain events and watershed analysis using other
methods directly into SWMM.
Use the Select buttons to browse to the correct surface and network files. Set the desired Units, Flow Routing Method and Force Main Equation. Choose the physical processes to include in the analysis. Choose whether to skip Steady State analysis or not. If skipped, set the System Flow Tolerance and the Lateral Flow Tolerance percentages. Finally, set the Simulation Start and End dates and times.
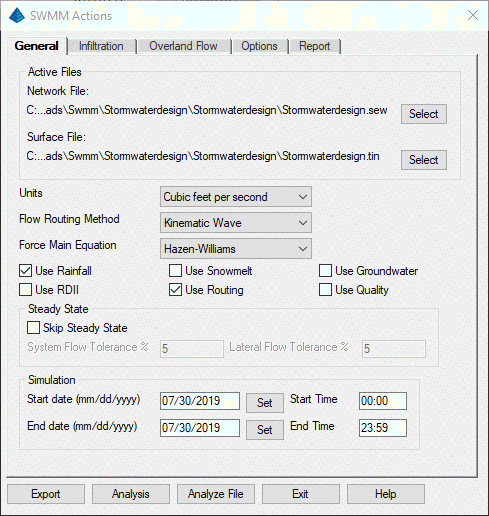
Selecting the Infiltration tab allows the user to choose one of five Infiltration Models and exposes input parameters specifically needed for the Model selected. Parameters for Models not selected are grayed out.
Use the Select buttons to browse to the correct surface and network files. Set the desired Units, Flow Routing Method and Force Main Equation. Choose the physical processes to include in the analysis. Choose whether to skip Steady State analysis or not. If skipped, set the System Flow Tolerance and the Lateral Flow Tolerance percentages. Finally, set the Simulation Start and End dates and times.
Selecting the Infiltration tab allows the user to choose one of five Infiltration Models and exposes input parameters specifically needed for the Model selected. Parameters for Models not selected are grayed out.
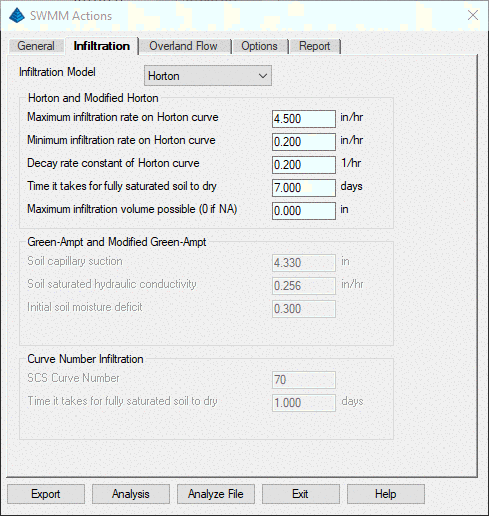
Selecting the Overland Flow tab allows the
user to set Manning's friction coefficients (n) for impervious and
pervious areas, depression storage depths, the percentage of
Impervious areas with no depression storage, and where Overland
Flow is routed, Pervious, Impervious or Outlet.
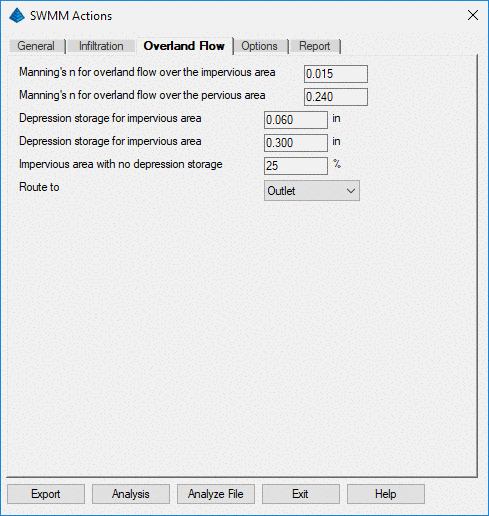
Selecting the Options tab allows the user
to enter additional parameters needed by SWMM for
analysis.
Sweep start and Sweep end are used reduce the accumulated buildup of specific pollutants with street sweeping.
Dry Days is the number of days with no rainfall prior to the start of the simulation.
Report Step is the interval for reporting of computed results.
Wet Step is the interval for computing runoff during rainfall and continuing until standing ponds and LID devices (Low Impact Development) are dry.
Dry Step is the time step length used for runoff computations when there is no rainfall or ponding and storage devices are dry - essentially to compute pollutant buildup. Dry Step must be greater than or equal to the Wet Step.
Routing Step is the time step length used for routing flows and quality constituents through the conveyance system.
Lengthening Step is used with Dynamic Wave Routing to artificially lengthen a conduit so that the travel time of a wave is greater than this time step (Courant stability criterion).
Variable Step is a safety factor applied to variable time steps computed using Dynamic Wave Routing.
Minimum Step is the shortest time step allowed when variable time steps are used with Dynamic Wave Routing.
Inertial Damping is used to control inertial terms in the Saint Venant momentum equation used in Dynamic Flow Routing. Choosing None uses these terms at all times, Partial reduces the terms as flow approaches critical and removes them when flow becomes supercritical, Full removes these terms from the equation.
Normal Flow Limited specifies which condition is checked to determine if conduit flow is supercritical and should be limited to normal flow using Dynamic Wave Routing. Use Slope to determine if water surface slope is greater than conduit slope. Use Froude to check if the Froude Number is greater than 1 or Both to check both conditions.
Minimum Surface Area is the minimum surface area used when computing water depth changes under Dynamic Wave Routing.
Minimum Slope is the minimum slope allowed for a conduit. Zero sets no minimum. SWMM uses a minimum of .001 ft drop during computations.
Head Tolerance is the difference at each node between successive trials. If the difference in head for a time step is less than this value, the flow solution has converged.
Maximum Trials is the maximum number of trials allowed during a time step to reach convergence when updating hydraulic heads at the system's nodes.
Number of Threads allows the user to increase the number of parallel processing threads used during Dynamic Wave Flow Routing if the computer being used has multi-core processors installed.
Sweep start and Sweep end are used reduce the accumulated buildup of specific pollutants with street sweeping.
Dry Days is the number of days with no rainfall prior to the start of the simulation.
Report Step is the interval for reporting of computed results.
Wet Step is the interval for computing runoff during rainfall and continuing until standing ponds and LID devices (Low Impact Development) are dry.
Dry Step is the time step length used for runoff computations when there is no rainfall or ponding and storage devices are dry - essentially to compute pollutant buildup. Dry Step must be greater than or equal to the Wet Step.
Routing Step is the time step length used for routing flows and quality constituents through the conveyance system.
Lengthening Step is used with Dynamic Wave Routing to artificially lengthen a conduit so that the travel time of a wave is greater than this time step (Courant stability criterion).
Variable Step is a safety factor applied to variable time steps computed using Dynamic Wave Routing.
Minimum Step is the shortest time step allowed when variable time steps are used with Dynamic Wave Routing.
Inertial Damping is used to control inertial terms in the Saint Venant momentum equation used in Dynamic Flow Routing. Choosing None uses these terms at all times, Partial reduces the terms as flow approaches critical and removes them when flow becomes supercritical, Full removes these terms from the equation.
Normal Flow Limited specifies which condition is checked to determine if conduit flow is supercritical and should be limited to normal flow using Dynamic Wave Routing. Use Slope to determine if water surface slope is greater than conduit slope. Use Froude to check if the Froude Number is greater than 1 or Both to check both conditions.
Minimum Surface Area is the minimum surface area used when computing water depth changes under Dynamic Wave Routing.
Minimum Slope is the minimum slope allowed for a conduit. Zero sets no minimum. SWMM uses a minimum of .001 ft drop during computations.
Head Tolerance is the difference at each node between successive trials. If the difference in head for a time step is less than this value, the flow solution has converged.
Maximum Trials is the maximum number of trials allowed during a time step to reach convergence when updating hydraulic heads at the system's nodes.
Number of Threads allows the user to increase the number of parallel processing threads used during Dynamic Wave Flow Routing if the computer being used has multi-core processors installed.
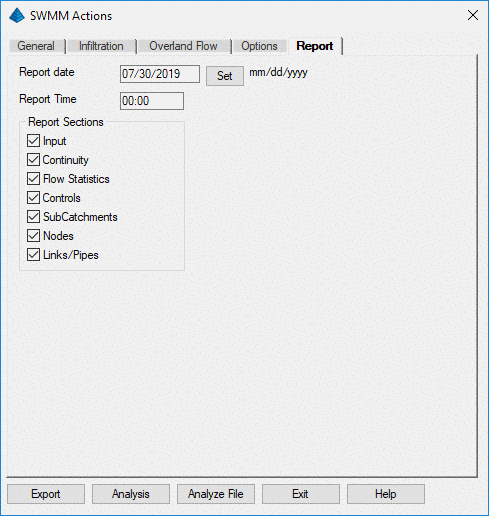
Selecting the Report tab allows the user
to specify the report date and time as well as to select the Report
Sections to be included.
The Export button exports an .inp file to
be opened in EPA SWMM software.
The Analysis button creates a report within Carlson software for review and error checking.
The Analyze File button allows the user to open an existing .inp file and displays the Carlson analysis report.
Exit closes the SWMM Actions dialog.
Pulldown Menu Location: Network
Keyboard Command: swmm
Prerequisite: SWMM version 5.1
The Analysis button creates a report within Carlson software for review and error checking.
The Analyze File button allows the user to open an existing .inp file and displays the Carlson analysis report.
Exit closes the SWMM Actions dialog.
Pulldown Menu Location: Network
Keyboard Command: swmm
Prerequisite: SWMM version 5.1