If
Time Period Analysis - Single is
selected, all other fields on the tab are deactivated, setting up a
"snapshot" analysis of the pressure pipe network.
If
Time Period Analysis - Extended is selected, all fields
on the tab are available for edit.
Total Duration is
the total length of time to be analyzed. Water quality is not
currently being analyzed in Carlson 2019.
Quality Time
Step is not currently used.
Pattern Start Time is
the time the
Demand Patterns created and listed on the
"Demand Patterns" tab starts.
Report Start Time is the first
time shown on the analysis.
Hydraulic Time Step is the
time unit incremented as the analysis proceeds through the
Total Duration. Pattern Time Step is the time unit
used to step from one
Demand Pattern to the next.
Reporting Step Time defaults to the
Hydraulic Time
Step unless and different increment is assigned in this
field.
Clock Start Time is when the analysis
begins. The
Statistic controls how information is
presented in the
Analysis report.
None reports
data at each
Reporting Time Step increment or, if zero, the
Hydraulic Time Step.
Average reports the
average values found for the
Total Duration.
Minimum reports the minimum value,
Maximum reports
the maximum value and
Range reports minimum and maximum
values across the
Total Duration.
The "Demand Patterns" tab allows the weighting of water demand
assigned to connections and laterals when creating the pressure
pipe network based on time of day.
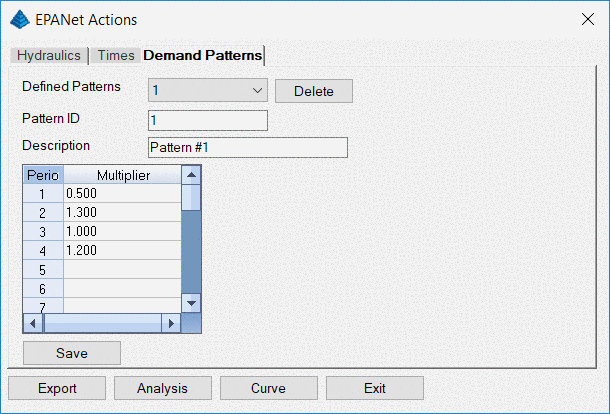
Select an existing pattern to be used to weight
the demand during different times of the day. To add a new
Pattern, type a new
Pattern ID, a new
Description,
desired
Multipliers and click
Save.
In the example above, the Clock and the Pattern start at midnight
and the demand is reduced by the
Multiplier 0.50 until the
Pattern Time Step increment comes due at 6am, increasing the
demand by 1.3. At noon, demand drops to its' default values,
then at 6pm demand is increased by a factor of 1.20. Note
that the
Pattern Time Step and the number of
Multipliers are synchronized.
Next, develop a pump curve by clicking the
Curve button. By
specifying the
Type, the values in the X and Y columns are
defined.
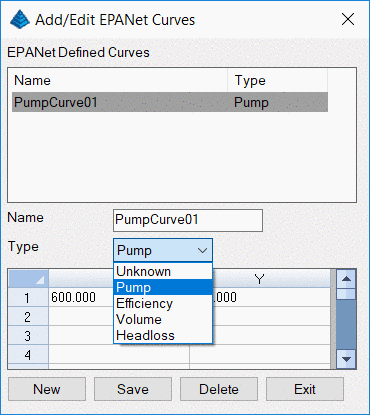
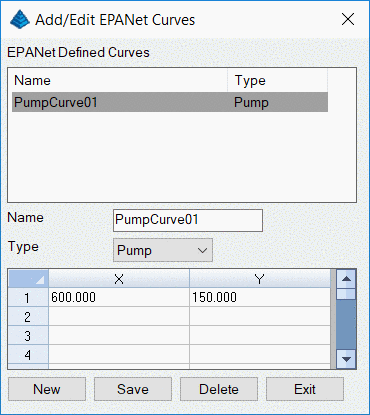
The Curve Type Pump develops a
single-point or multi-point Pump Curve plotting
volume per unit time (flow rate) in the X column, head in the Y
column. An Efficiency Curve plots a pump's flow rate in the
X column vs. energy use efficiency as a percentage in the Y
column. A Volume Curve plots flow rate in the X column
vs. the change in elevation (head) in a tank and is used to model
tanks with non-uniform cross sections. A Headloss
Curve plots the flow rate in the X column vs. the headloss in
feet or meters in the Y column as water flows through a General
Purpose Valve.
The Analysis button produces a report that can be viewed,
saved, printed and search showing demands, flow rates, head, energy
consumption, pressures, velocities and headlosses in the Network,
either as a snapshot or with a Demand Pattern applied.
The Export button creates a file which can be imported into
EPANet.
Pulldown Menu Location: Network
Keyboard Command: epanet
Prerequisites: Centerline files, Profile files and/or
polylines representing pipes, pumps, and valves.