In addition to providing a graphical method for displaying feature-rich data located anywhere on the globe, Google Earth also provides the ability for software applications to extract its underlying terrain data. While the elevational accuracy of the Google Earth surface should be considered extremely coarse, it might be suitable for large-scale watershed modeling studies, preliminary land-planning studies or "proof-of-concept" preliminary designs.
When extracting terrain data from Google Earth, it is important to keep "diminishing returns" in mind. As an example, a land surveyor might perform a traditional grid-based topographic survey by sampling the land every 50 feet. Although a 25 foot grid spacing would yield more accurate results than a 50 foot grid, it would typically take at least twice as long to survey. Harvesting terrain data from Google Earth operates in a similar fashion:
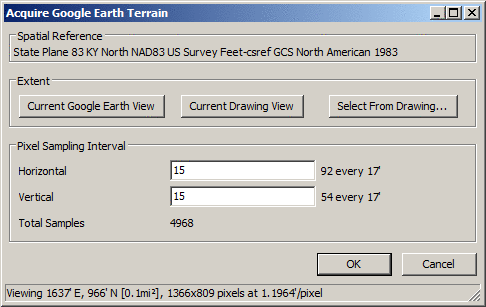
Consider the following example. Based on the physical screen size of the Google Earth application and the "zoom" (or "view") resolution of a project site, the following values (summarized at the bottom of the dialog box) were returned:

| Unit | Horizontal | Vertical |
|---|---|---|
| Feet | 1637 | 966 |
| Pixels | 1366 | 809 |
| Feet/Pixel | 1.19 | 1.19 |
In the sample above, the total area is calculated and displayed (0.1 mi2) along with the desired "projection" system for our project site. Although it might be desired to sample every pixel in this project... 1,107,270 = (1366+1)*(809+1), in all, the "point of diminishing return" would be quickly reached and could clog Google servers with extraneous terrain requests; see the NOTE section below.
Spatial Reference: Displays the spatial reference coordinate projection system of the current drawing. The projection can be set using the Drawing Setup command.
Extent - Current Google Earth View: Gets the overall dimensions of the Google Earth session and displays the results in both pixels and the appropriate units of measure.
Extent - Current Drawing View: Gets the overall dimensions of the current CAD view and displays the results in both pixels and the appropriate units of measure.
Extent - Select from Drawing: Sets the overall dimensions of the Google Earth session to conform with a drawing window from CAD and displays the results in both pixels and the appropriate units of measure.
Pixel Sampling Interval: Allows the ability to indicate how often a pixel row or column should be sampled for terrain elevation. Smaller intervals result in higher total samples and longer processing time.
Consider the following "sample" diagram:
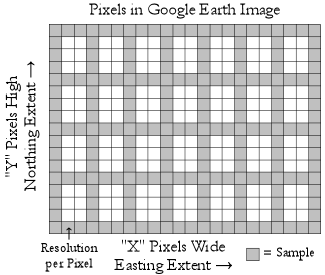
Referring back to our horizontal and vertical samples shown in the dialog box above, we are requesting:
| Requesting | Horizontal | Vertical |
|---|---|---|
| Pixel Interval | 15 | 15 |
| Samples | 92 = Int(1366/15)+1 | 54 = Int(809/15)+1 |
| Sample Every | 17 ft (approx.) = Int(1637/92) | 17 ft (approx.) = Int(966/54) |
The resulting total samples 4968 = (92)*(54) and it is recommended that this value be at or below the Google Earth session threshold of 5000.
Identify
first corner: Identify one
corner of a drawing window that should be used to set the Google
Earth display
Identify opposite corner: Identify the opposite corner of a drawing window that
should be used to set the Google Earth display
Pulldown Menu Location:
Civil > Surface > Import/Export
Surface, Survey > Surface >
Import/Export Surface, Takeoff >
Tools > Import/Export, Construction > Import/Export
Keyboard Command: gesurface
Prerequisite: Coordinate projection system, Functioning
version of Google Earth with Terrain enabled, Internet
connection